Multimedia and geographic data integration for cultural heritage information retrieval
Master Thesis project
In the thesis project, I developed a system providing the integration between Content-Based Image Retrieval (CBIR) and Geographic Information Retrieval (GIR). My work aimed to prove that the use of geographic data can improve the results obtained by an image matching system based only on multimedia/visual data.
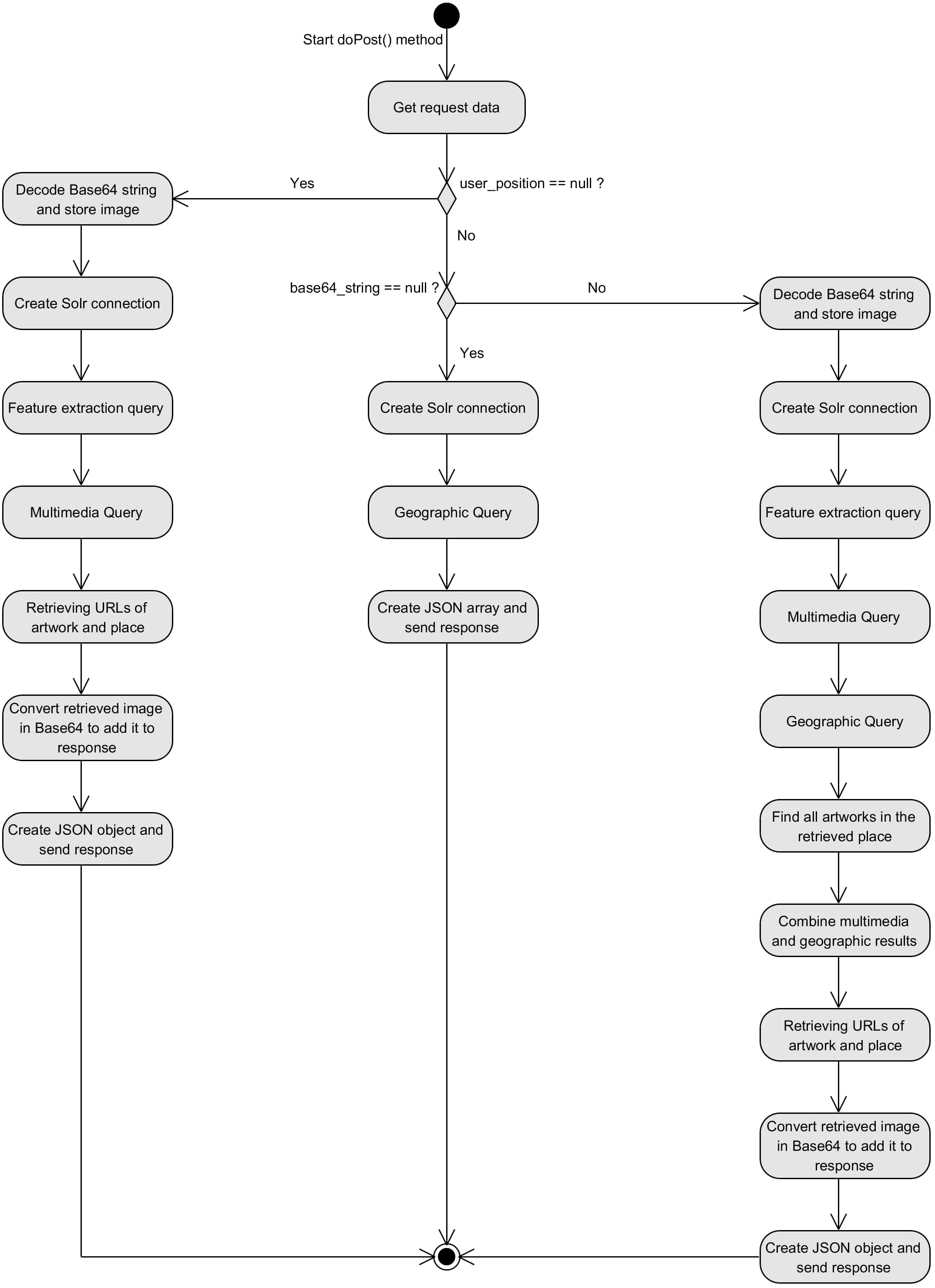
This work is part of a wide project about cultural heritage, in which a mobile application that helps users to retrieve information about artworks and museums has been developed. The logic architecture is shown in the figure below where the highlighted components represent the area I implemented.
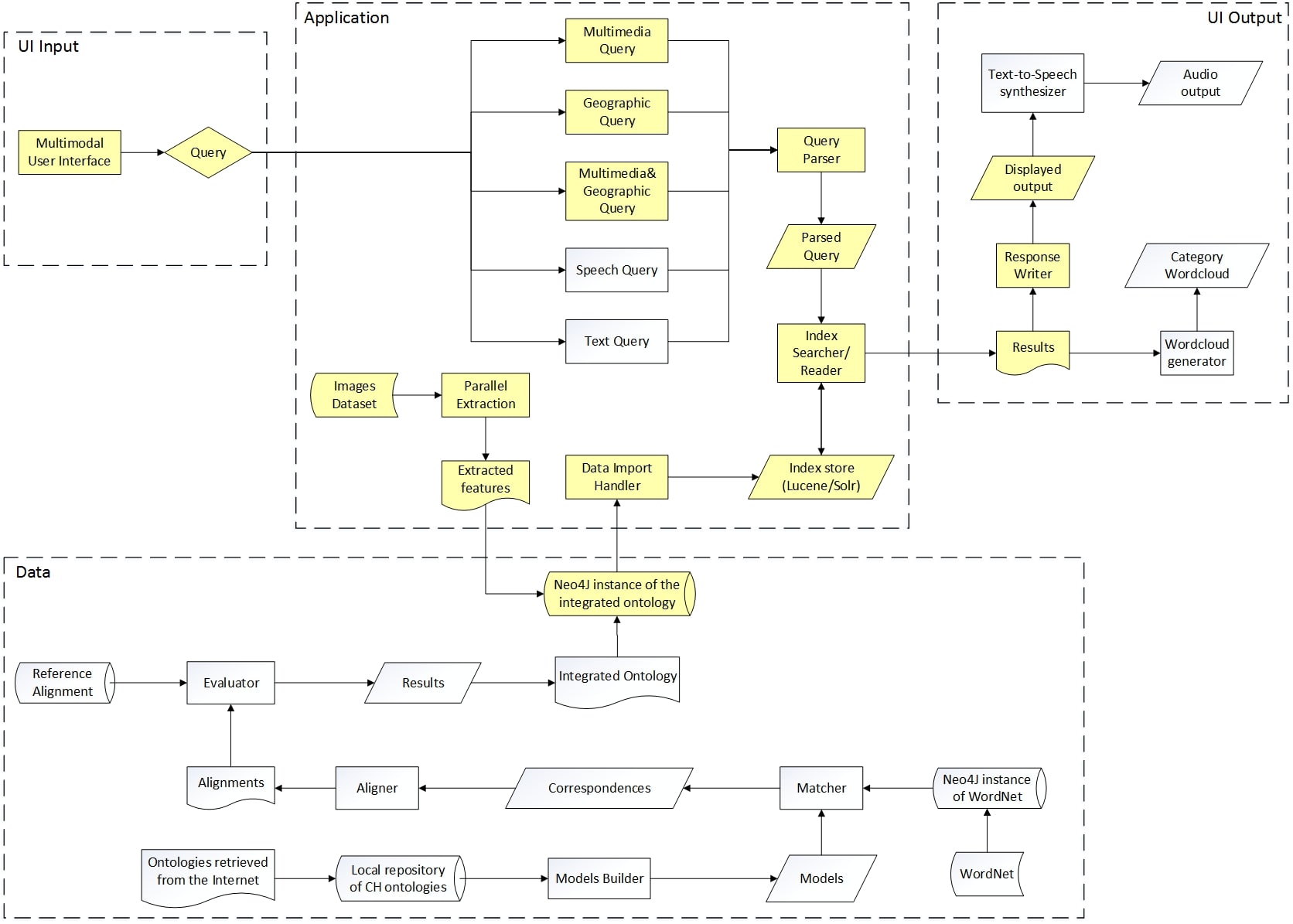
Functionalities implemented
The system is composed by three functionalities:
-
Multimedia Query: the principal aim of Content-Based Image Retrieval is to develop techniques for retrieving images on the basis of automatically-derived features; for this motivation, this functionality provides to:
- Extract multimedia/visual features from an image previously loaded;
- Perform a search by the features vector obtained as result of the extraction.
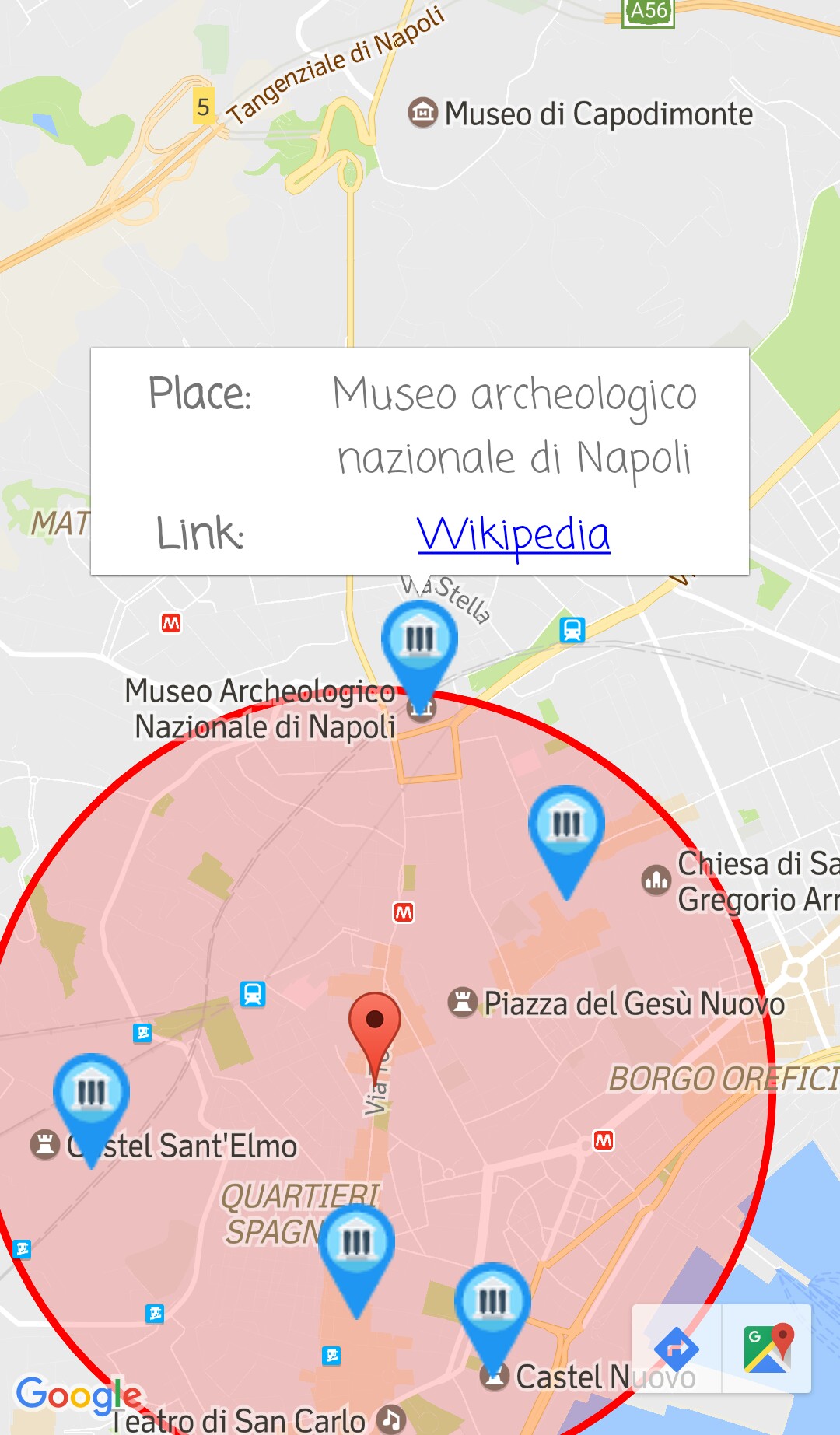
- Geographic Query: it consists in a points of interest (POI) search and, considering that this is a system about cultural heritage, a point of interest can be represented by a museum, a church, an art gallery. In particular, for this functionality, I chose museums as POIs. To perform this type of search, a radius has to be set to define the circle in which the museums can be retrieved.
- Multimedia&Geographic Query: the idea of combining geographic data with multimedia data comes from observation of Multimedia Query results. Most of the artworks submitted to the system were retrieved as second, third or fourth result, and I noted that, in the position of the ranking that preceded them, there were always (or almost) artworks sited in different places than the considered ones. So, I decided to try to improve the image retrieval, more precisely the image matching, developing a functionality based on the geolocation of the user who perform the retrieval query, that would filter the results of a standard Multimedia Query. Obviously, filtering is possible only if the user geographic position is available at real-time, thus this is a function oriented to mobile devices.
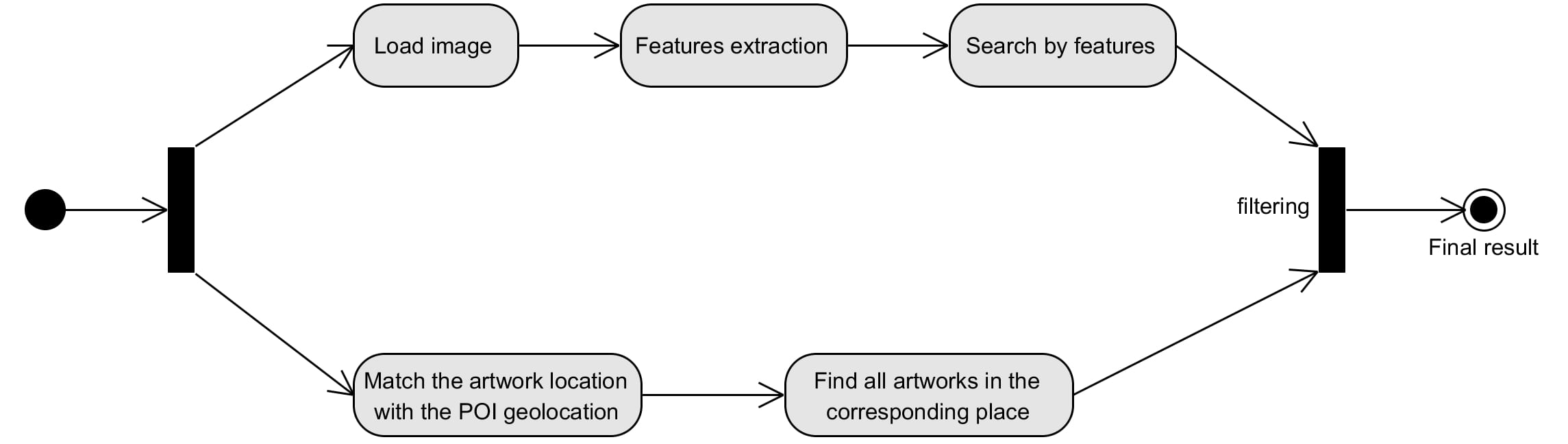
The Multimedia&Geographic Query is the core functionality and consists of the following steps:
- The first steps are equals to Multimedia Query and have the same purpose;
- A Geographic Query is performed to match the artwork location, based on the user geographic position, with the corresponding POI geolocation, in order to discover the place in which the user, and thus the artwork, is located;
- The result of the previous query is used to find all the artworks in that place;
- List of artworks is used in order to filter the multimedia results and obtain better response values.
Technological architecture
The following image displays the technologies used to implement the functionalities previously illustrated. The hidden parts represent technologies employed by other component of the entire cultural heritage system and not used in this work.
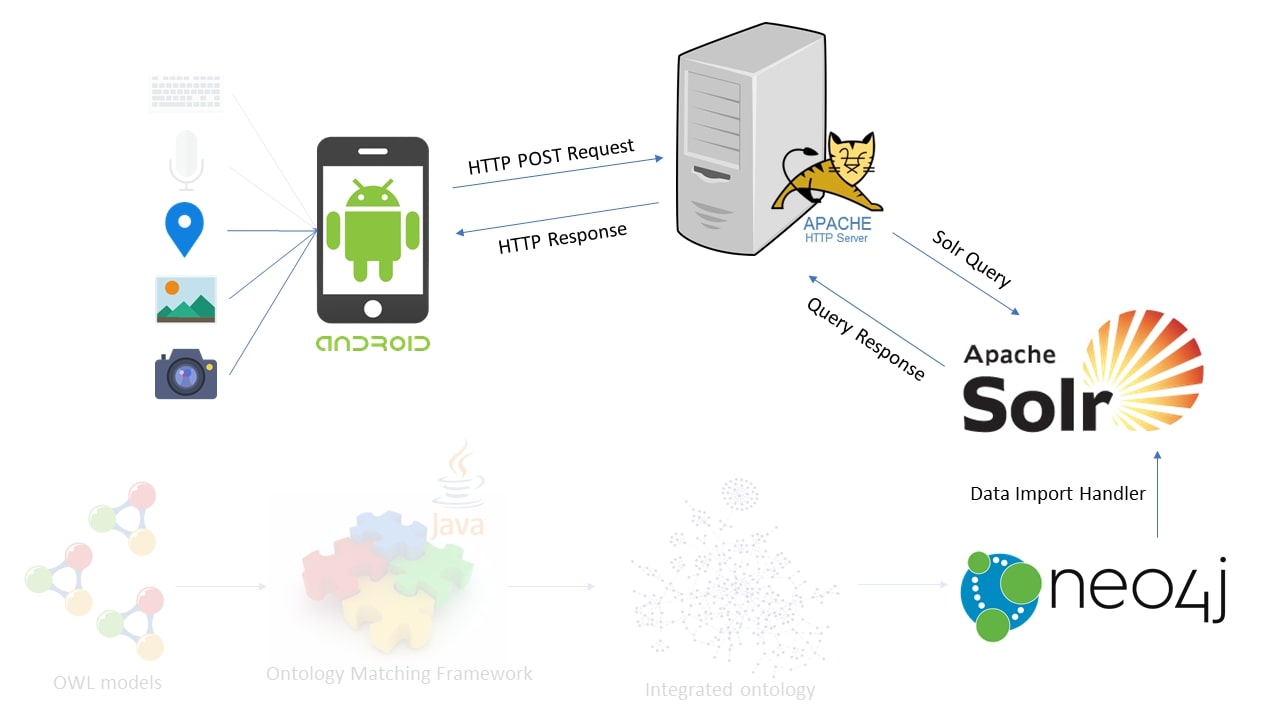
Main tools employed:
Application design
The described system has been designed with a client-server architecture.
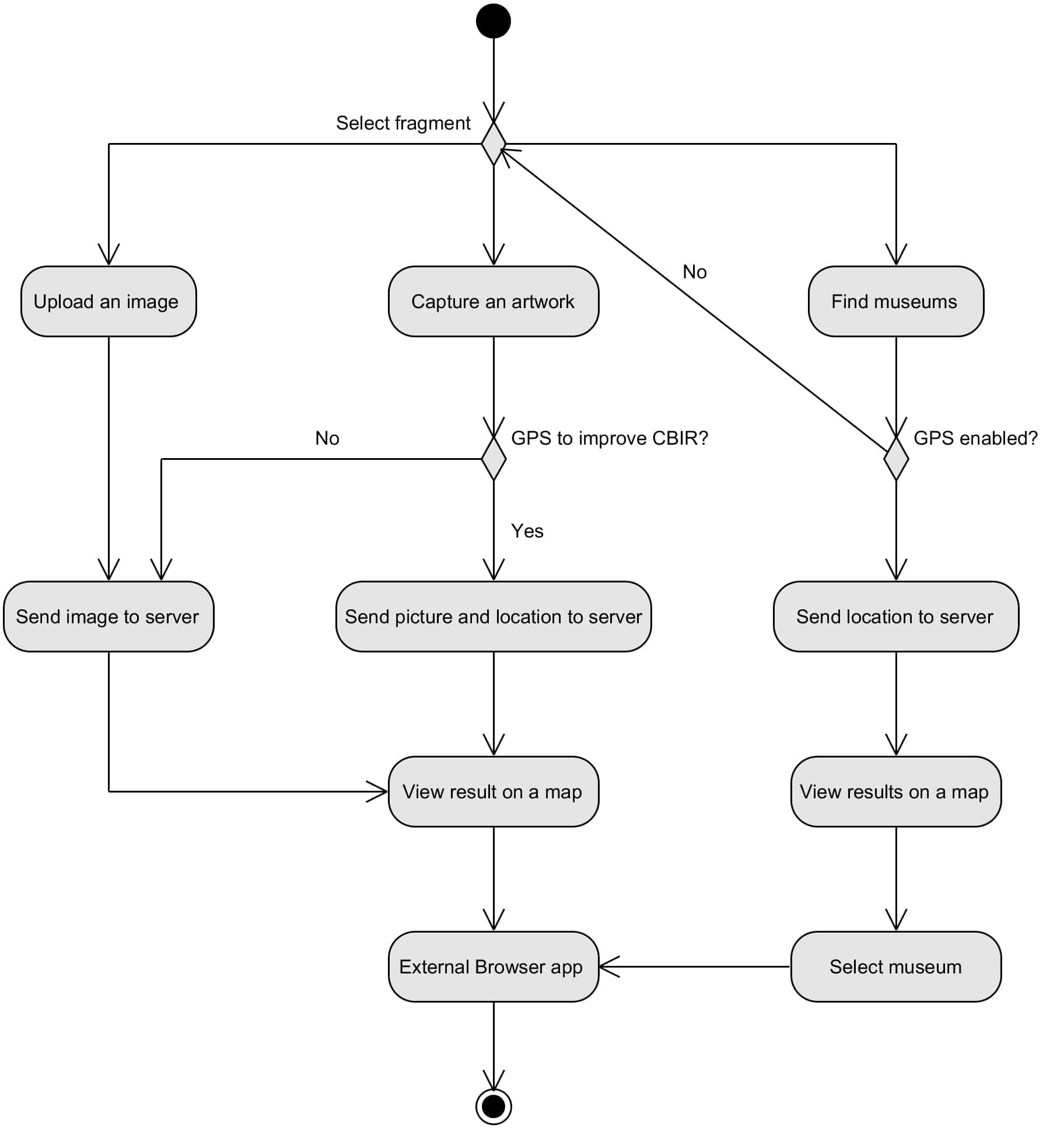
The client-side application allows users to:
- Upload an image from device gallery to retrieve information about the represented artwork;
- Take a picture of an artwork in a POI to retrieve information about it. The user can enable his position given by GPS sensor to improve the information retrieval;
- Discover the location of the museums closest to him.
The server-side system is able to:
- Receive and manage data sent by client application to call the right method, based on data types received in the request;
- Establish the connection with the
SolrClient; - Perform the necessary
SolrQuery; - Get results as
SolrDocument; - Send the response to client.
Dataset
I considered a selection of paintings and sculptures from six museums of Naples:
- Museo Nazionale di Capodimonte
- Gallerie di Palazzo Zevallos Stigliano
- Museo Nazionale di San Martino
- Museo Cappella Sansevero
- Museo Archeologico Nazionale di Napoli
- Museo Civico di Castel Nuovo
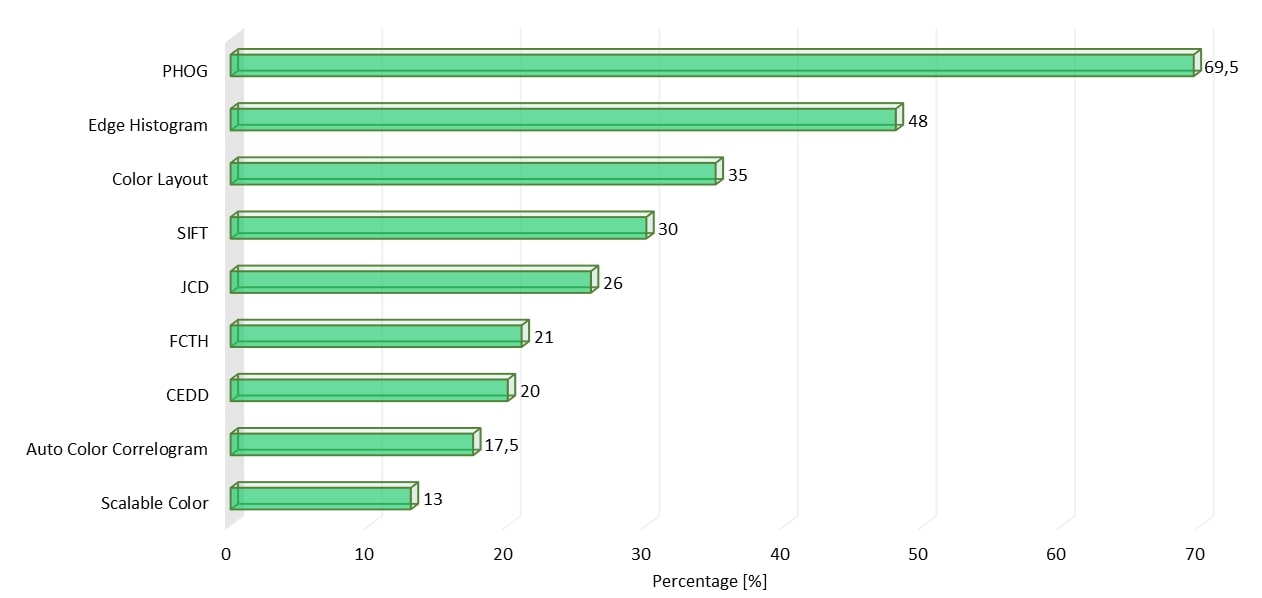
Features evaluation
A subset of global and local features proposed in literature have been proposed and tested to analyse their performances to select the best for the final system implementation:
- Pyramid of Histograms of Orientation Gradients (PHOG)
- Auto Color Correlogram
- MPEG-7 Scalable Color Descriptor
- MPEG-7 Color Layout Descriptor
- MPEG-7 Edge Histogram Descriptor
- Fuzzy Color and Texture Histogram (FCTH)
- Color and Edge Directivity Descriptor (CEDD)
- Joint Composite Descriptor (JCD)
- Scale Invariant Feature Transform (SIFT)
For each feature, I extracted the value of every image in the dataset and evaluated the exact match between resulting and actual artwork. Results showed PHOG as the most performing feature and this descriptor has been used for the development of the mobile application.
System evaluation
The system has been evaluated “on the field” in the three museums that granted the availability for testing:
- Museo Nazionale di Capodimonte
- Gallerie di Palazzo Zevallos Stigliano
- Museo Nazionale di San Martino
For each artwork in the dataset and located in those places, both Multimedia Query and Multimedia&Geographic Query functionalities have been evaluated. The results are displayed below and they show a visible and quantifiable improvement in the integration of geographic and multimedia data, with a positive difference of 32.65%.

Android application
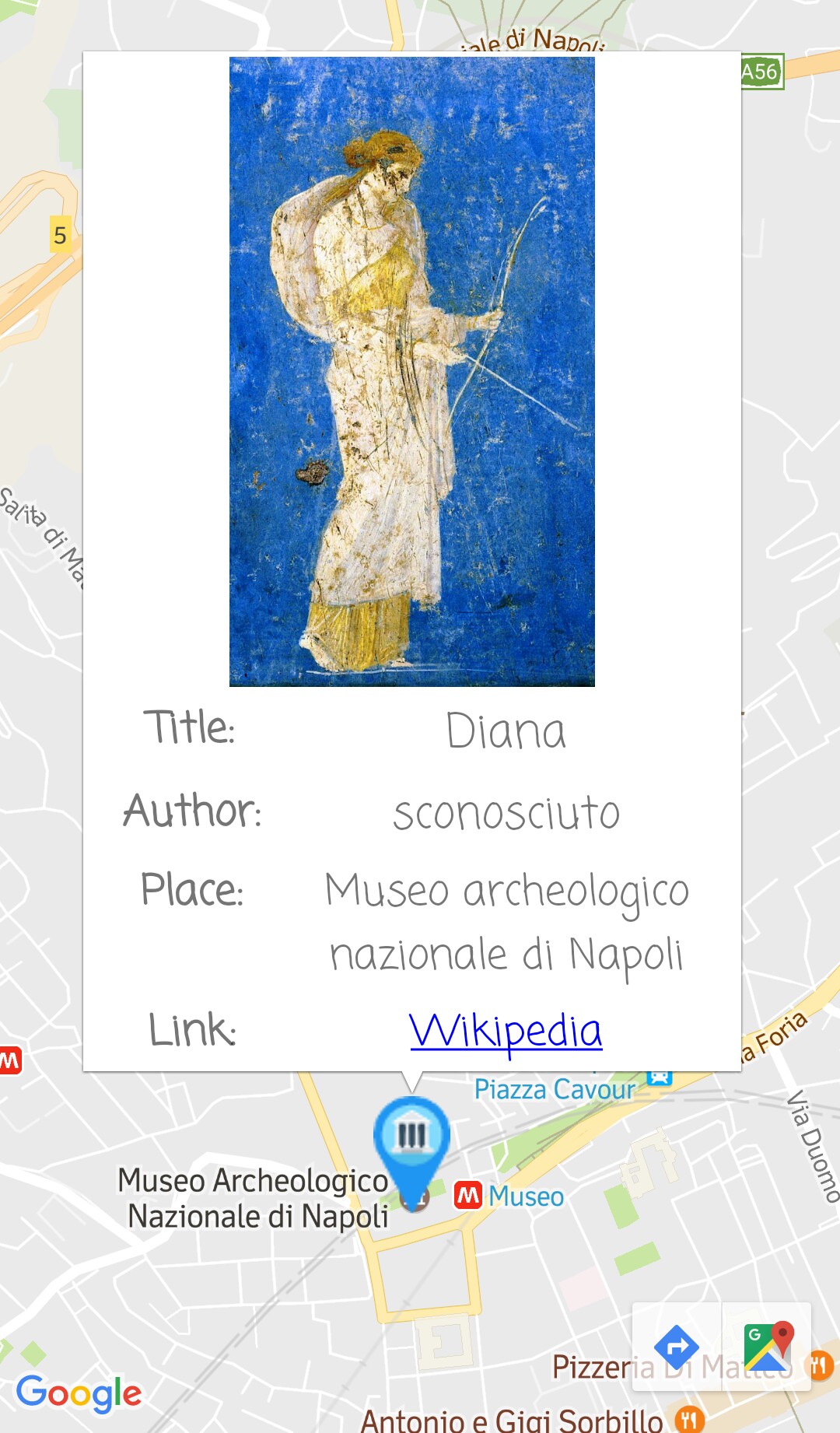
The mobile application implements the three available tasks of the client-side described above:
- Upload an image: image loaded from the device gallery;
- Capture an artwork: picture taken by camera and optionally results improved by GPS location;
- Find museums: discover the location of the closest museums.






References
This work has been published in two papers:
- Purificato, Erasmo, and Antonio M. Rinaldi. Multimedia and geographic data integration for cultural heritage information retrieval. Multimedia Tools and Applications 77.20 (2018): 27447-27469.
- Purificato, Erasmo, and Antonio M. Rinaldi. A multimodal approach for cultural heritage information retrieval. International Conference on Computational Science and Its Applications. Springer, Cham, 2018.